Simulation of Pearl-Chain Formation of Microparticles by Acoustic Standing Waves, including Inter-Particle Forces and Collisions
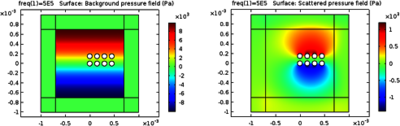
Acoustic standing waves can be used to manipulate micrometer sized particles, cells and organisms. In most applications these objects are driven towards pressure nodal lines, predominantly by the primary acoustic radiation force. Interestingly, at intermediate particle concentrations, detailed phenomena of line-formation and inter-line repulsion occur. Such phenomena are believed to be caused by secondary (inter-particle) acoustic forces, initially not observable due to the movement of particles toward the nodal line, they become apparent close to the nodal line. In addition to attractive and repulsive interactions, collisions between particles play an important role in the pattern formation and should be included in numerical simulations. In this work, we use COMSOL Multiphysics® and MATLAB® to solve the multi-scattering problem and acquire the acoustic radiation force numerically. Our method allows us to analyze complex acoustic particle interactions, effectively explaining particle chain formation.
Téléchargement
- baasch_presentation.pdf - 1.11MB
- baasch_abstract.pdf - 0.26MB
