La Bibliothèque d'Applications présente des modèles construits avec COMSOL Multiphysics pour la simulation d'une grande variété d'applications, dans les domaines de l'électromagnétisme, de la mécanique des solides, de la mécanique des fluides et de la chimie. Vous pouvez télécharger ces modèles résolus avec leur documentation détaillée, comprenant les instructions de construction pas-à-pas, et vous en servir comme point de départ de votre travail de simulation. Utilisez l'outil de recherche rapide pour trouver les modèles et applications correspondant à votre domaine d'intérêt. Notez que de nombreux exemples présentés ici sont également accessibles via la Bibliothèques d'Applications intégrée au logiciel COMSOL Multiphysics® et disponible à partir du menu Fichier.
This application shows how mass transfer out from a thin 3D domain can be approximated using a 2D component with the domain feature Out-of-Plane Flux. This feature is useful when the concentration gradient in the out-of-plane direction (along the thickness) is small, and decreasing the ... En savoir plus
This model simulates convective heat transfer in a channel filled with water. To reduce memory requirements, the model is solved repeatedly on a pseudo-periodic section of the channel. Each solution corresponds to a different section, and before each solution step the temperature at the ... En savoir plus
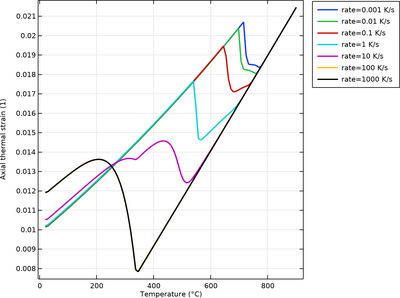
In this example, phase transformation data and phase material properties are imported from JMatPro, and used to compute CCT curves. Dilatometry curves (axial thermal strain) are computed across a range of cooling rates. En savoir plus
This example exemplifies how to model the Beer-Lambert law using the core functionality of COMSOL Multiphysics. A more detailed description of the phenomenon and the modeling process can be seen in the blog post "Modeling Laser-Material Interactions with the Beer-Lambert Law". En savoir plus
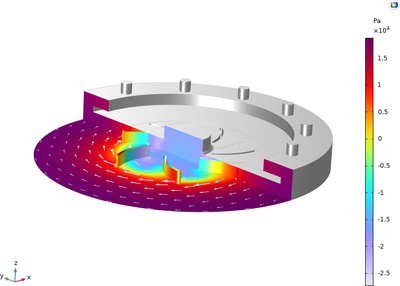
A lab-on-a-chip platform can be realized on a rotating disc by designing channels and other features to use the Coriolis or centrifugal forces to manipulate the flow. These forces are controlled by changing the angular velocity of the disc, so the platform is programmed by using a ... En savoir plus
The model shows how to estimate the Young's modulus and Poisson ratio based on a tensile test. The test measures the tensile force and the radial displacement for different values of the prescribed displacement. The model is based on synthetic data generated in the model itself. It is ... En savoir plus
The present example simulates the steady-state flow in a radial pump using the mixing plane methodology. It solves for the averaged flow resulting from different blade positions of the rotor, thus circumventing the need to perform costly time-dependent simulations. En savoir plus
One way to design a filter is to use the element values of well-known filter prototypes, such as maximally flat or equal-ripple low-pass filters. It is easier to fabricate a distributed element filter on a microwave substrate than a lumped element filter, since it is cumbersome to find ... En savoir plus
Multiscale modeling is a challenging issue in modern simulation. This occurs when there are vastly different scales in the same model. For example, your cell phone is approximately 10 cm, yet it receives GPS information from satellites 20,000 km away. In these models we examine several ... En savoir plus
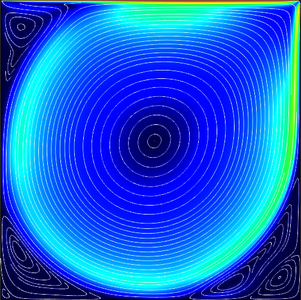
This example demonstrates how to define the lid-driven cavity benchmark in the field of computational fluid dynamics. In the model setup, a 2D square cavity has a tangentially moving wall that induces a large vortex in the center of the cavity, and small vortices in the corners. The ... En savoir plus