La Bibliothèque d'Applications présente des modèles construits avec COMSOL Multiphysics pour la simulation d'une grande variété d'applications, dans les domaines de l'électromagnétisme, de la mécanique des solides, de la mécanique des fluides et de la chimie. Vous pouvez télécharger ces modèles résolus avec leur documentation détaillée, comprenant les instructions de construction pas-à-pas, et vous en servir comme point de départ de votre travail de simulation. Utilisez l'outil de recherche rapide pour trouver les modèles et applications correspondant à votre domaine d'intérêt. Notez que de nombreux exemples présentés ici sont également accessibles via la Bibliothèques d'Applications intégrée au logiciel COMSOL Multiphysics® et disponible à partir du menu Fichier.
Lead-acid batteries are widely used as starting batteries for various traction applications such as cars and trucks and so forth. The reason for this is the fairly low cost in combination with the performance robustness for a broad range of operating conditions. However, one drawback of ... En savoir plus
This app demonstrates the usage of a surrogate model function for predicting the cell voltage, cell open circuit voltage and internal resistance of an NMC111/graphite battery cell undergoing a battery test cycle. The surrogate function, a Deep Neural Network, has been fitted to a ... En savoir plus
This model shows how to set up a 3D simulation of a n-p-n bipolar transistor. It is a 3D version of the device shown in the Bipolar Transistor model, and demonstrates how to extend semiconductor modeling into 3D using COMSOL Multiphysics. As in the 2D version of this model, the device ... En savoir plus
This model reproduces the NiCd battery model and the results presented in De Vidts' and White's paper from 1995. Ref: P. De Vidts, R. E. White, “Mathematical Modeling of a Nickel-Cadmium Cell: Proton Diffusion in the Nickel Electrode”, J. Electrochem. Soc, Vol. 142, No. 5, May 1995. En savoir plus
Combinations of optical devices such as polarizers and wave retarders can be used to control the intensity and polarization of transmitted radiation. In this tutorial, two linear polarizers with orthogonal transmission axes are used to reduce the intensity of a ray to zero. Then the ... En savoir plus
For a description of this model, see our accompanying blog post "Can COMSOL Multiphysics® Solve the Hydrogen Atom?". En savoir plus
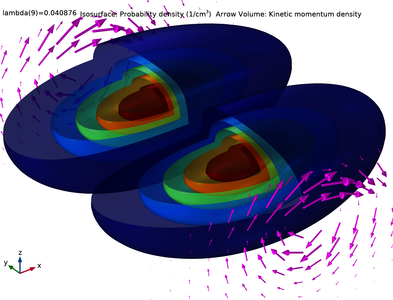
This tutorial model solves a two-component Schrödinger equation for the eigenstates of a simple silicon quantum dot in a uniform magnetic field, based on the paper by Jock et al. on the topic of spin-orbit qubits. The built-in domain condition Lorentz Force for the Schrödinger Equation ... En savoir plus
This tutorial compares experimental data from the literature with a COMSOL model of a MOSCAP with interface traps (surface states). The Trap-Assisted Surface Recombination feature is used to simulate the effects of the trap charges and the processes of carrier capturing and emitting by ... En savoir plus
This benchmark model simulates a graded heterojunction using the thermionic emission formulation for the charge transfer over the junction. It shows the additional contribution to the current density from the quantum tunneling effect across the potential barrier, using the WKB ... En savoir plus
This example demonstrates how to model the temperature distribution in a battery pack during a 4C discharge. The pack is constructed by first coupling two cylindrical batteries in parallel. Six parallel-connected pairs are then connected in series to create the full pack. (This is also ... En savoir plus