Electrodeposition of a Microconnector Bump in 2D
Application ID: 11682
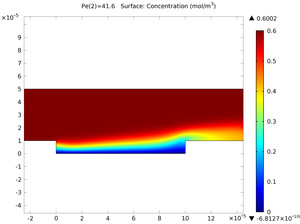
This model demonstrates the impact of convection and diffusion on the transport-limited electrodeposition of a copper microconnector bump (metal post). Microconnector bumps are used in various types of electronic applications for interconnecting components, for instance liquid crystal displays (LCDs) and driver chips.
The location of the bumps on the electrode surface is controlled by the use of a photoresist mask. Control of the current distribution in terms of uniformity and shape is important for ensuring the shape and resulting reliability of the interconnector bumps.
The cell is running at a high overpotential so the deposition rate is governed by the transport rate of the depositing ion in the electrolyte. A result of this operating condition is that the electric potentials in the electrolyte and electrode need not be modeled to determine the current distribution on the bump. The model is based on a paper by Kondo and others.
This model example illustrates applications of this type that would nominally be built using the following products:
however, additional products may be required to completely define and model it. Furthermore, this example may also be defined and modeled using components from the following product combinations:
The combination of COMSOL® products required to model your application depends on several factors and may include boundary conditions, material properties, physics interfaces, and part libraries. Particular functionality may be common to several products. To determine the right combination of products for your modeling needs, review the Grille des Spécifications and make use of a free evaluation license. The COMSOL Sales and Support teams are available for answering any questions you may have regarding this.



