HAMSTAD Benchmark 1: Heat and Moisture Transport in an Insulated Roof
Application ID: 75601
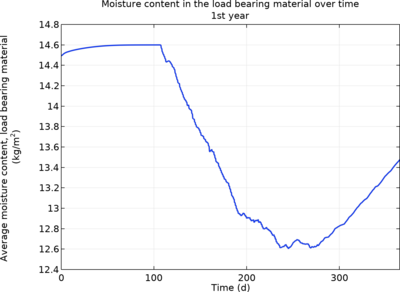
This tutorial demonstrates how to simulate coupled heat and moisture transport in an insulated roof structure composed of a load-bearing layer and an insulation layer. The thermal insulation faces the interior, while a moisture barrier is placed on the exterior side. The load-bearing layer is capillary-active, whereas the insulation layer is capillary-inactive. This difference leads to elevated relative humidity levels at the interface between the two materials, resulting in internal condensation.
The 1D model corresponds to the first benchmark defined in HAMSTAD-WP2 Modeling for validating numerical simulations of coupled heat and moisture transport in building materials.
A more detailed description of the physical phenomena and modeling approach is provided in the blog post Verifying a HAMSTAD Benchmark for an Insulated Roof Model.
This model example illustrates applications of this type that would nominally be built using the following products:
however, additional products may be required to completely define and model it. Furthermore, this example may also be defined and modeled using components from the following product combinations:
- COMSOL Multiphysics® et
- soit le Module Heat Transfer, ou Module Porous Media Flow
The combination of COMSOL® products required to model your application depends on several factors and may include boundary conditions, material properties, physics interfaces, and part libraries. Particular functionality may be common to several products. To determine the right combination of products for your modeling needs, review the Grille des Spécifications and make use of a free evaluation license. The COMSOL Sales and Support teams are available for answering any questions you may have regarding this.



