La Bibliothèque d'Applications présente des modèles construits avec COMSOL Multiphysics pour la simulation d'une grande variété d'applications, dans les domaines de l'électromagnétisme, de la mécanique des solides, de la mécanique des fluides et de la chimie. Vous pouvez télécharger ces modèles résolus avec leur documentation détaillée, comprenant les instructions de construction pas-à-pas, et vous en servir comme point de départ de votre travail de simulation. Utilisez l'outil de recherche rapide pour trouver les modèles et applications correspondant à votre domaine d'intérêt. Notez que de nombreux exemples présentés ici sont également accessibles via la Bibliothèques d'Applications intégrée au logiciel COMSOL Multiphysics® et disponible à partir du menu Fichier.
The Marangoni effect results in a slip velocity in the tangential direction on a fluid/fluid interface due to gradients in the surface tension coefficient. When the surface tension coefficient is constant, a two-fluid system may exist in static equilibrium. This is because the surface ... En savoir plus
In this tutorial model, a step thrust bearing is shape optimized to maximize the bearing capacity. A step thrust bearing consists of a stepped bearing surface on which the end of the shaft rotates. The entire assembly is submerged in a lubricant. The shaft collar is assumed to be ... En savoir plus
This app demonstrates the following: Parametric geometry containing a geometry sequence with if-statements to produce different types of designs Options to set the mesh size A graphical user interface that includes different windows that can be shown or hidden Light Theme Water ... En savoir plus
This model couples the Navier Stokes equations and the heat transfer equations to examine density driven flow of free fluids. Here the fluid is in a square cavity with a heated wall. The buoyancy force is a Boussinesq term added to the Navier-Stokes equations. The equation is ... En savoir plus
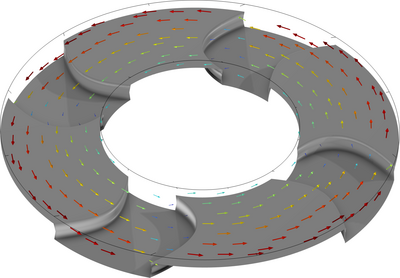
In this example, wear of the friction material in a disc brake is studied. Quasistatic friction forces are prescribed from simple kinematic considerations. The geometry of the brake pad is continuously updated to account for the material removal due to wear following the well-known ... En savoir plus
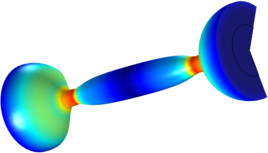
The eigenfrequencies of a rotating blade are studied in this benchmark. It shows how stress stiffening and the combined effect from stress stiffening and spin softening affects the fundamental eigenfrequency. High rotational speed in rotating machineries can result in centrifugal forces ... En savoir plus
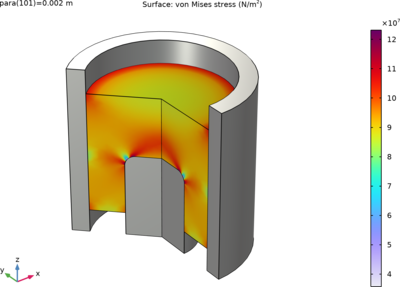
The fabrication of a cup through powder compaction is simulated in this tutorial model. The powder compaction process is becoming common in the manufacturing industry, due to its potential for producing components of complex shape and high strength. Combining the Fleck–Kuhn–McMeeking ... En savoir plus
This example demonstrates how to model a phase change and predict its impact on a heat transfer analysis. When a material changes phase, for instance from solid to liquid, energy is added to the solid. Instead of creating a temperature rise, the energy alters the material’s molecular ... En savoir plus
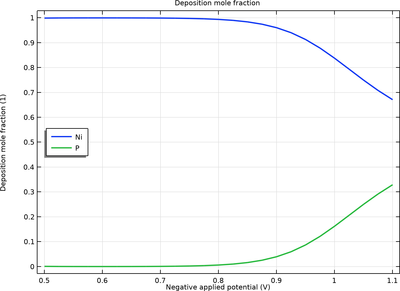
Electrochemical codeposition is a common low-cost method for producing metal alloys. This tutorial model demonstrates electrodeposition of a nickel (Ni)–phosphorous (P) alloy. The model accounts for charge and mass transport of a multitude of species along with multiple electrode ... En savoir plus
This is a model of a moving-coil loudspeaker where a lumped parameter analogy represents the behavior of the electrical and mechanical speaker components. The Thiele-Small parameters (small-signal parameters) serve as input to the lumped model, which is represented by an Electric Circuit ... En savoir plus