Ressources
Livres Blancs
- Bridging the Terahertz Gap
- Modeling the Lithium-Ion Battery
- Protection contre la Corrosion
- Modélisation des batteries
- Modélisation et Simulation dans le développement des piles à combustible
- Modélisation thermique des petits satellites
- Analyse électro-vibroacoustique d'un transducteur à armature équilibrée
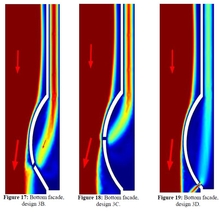
Assessing the Potential of Ventilated Facades on Reducing a Buildings’ Thermal Load Using Decoupled COMSOL Simulations
Publié en 2012
Solar radiation is a prominent contributor of energy in buildings, and can be transmitted directly into a building through opaque surfaces, but it can also be absorbed by building components (i.e. walls, roofs etc.). This study discusses the use and effect of ventilated facades, with an external facade cladding, a sub-structure anchored to the wall surface of the building under solar radiation, while designing facade elements numerically using COMSOL, to create the highest achievable velocity inside the air cavity. An improvement of up to 75% of the air velocity is reached in some parts of the cavity for the implemented design in comparison to the reference case.
Téléchargement
- schijndel3_presentation.pdf - 0.4MB
- schijndel3_poster.pdf - 0.44MB
- schijndel3_paper.pdf - 0.75MB
- schijndel3_abstract.pdf - 0.28MB



