- Bridging the Terahertz Gap
- Modeling the Lithium-Ion Battery
- Protection contre la Corrosion
- Modélisation des batteries
- Modélisation et Simulation dans le développement des piles à combustible
- Modélisation thermique des petits satellites
- Analyse électro-vibroacoustique d'un transducteur à armature équilibrée
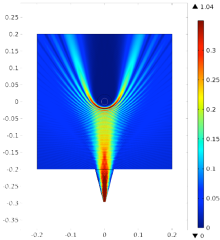
Scattering of mm-Waves by Turbulent Structures in Magnetically Confined Fusion Plasmas
In magnetically confined fusion devices, electron cyclotron resonance heating (80-170 GHz) is characterized by a local RF-power deposition at the electron cyclotron resonance [1]. A mm-wave RF Gaussian beam is launched from a dedicated antenna and propagates through the highly turbulent scrape-off layer (SOL) at the edge of the confined plasma. Turbulence in the SOL is characterized by filamentary plasma structures, known as blobs, which may affect the mm-wave propagation and lead to less precise targeting or broadening of the absorption at the resonant layer.
The RF Module of COMSOL Multiphysics® software is used to perform a full wave simulation of the scattering of the mm-waves by blobs. This allows investigating the interaction between the mm-waves and the turbulence in the SOL. The simulation results are compared with experiments carried out in TORPEX, a simple magnetized toroidal plasma with a magnetic configuration similar to the SOL, which enables the generation of blobs and their study [2].
Téléchargement
- chellaï_poster.pdf - 4.79MB
- chellaï_abstract.pdf - 0.02MB



