- Bridging the Terahertz Gap
- Modeling the Lithium-Ion Battery
- Protection contre la Corrosion
- Modélisation des batteries
- Modélisation et Simulation dans le développement des piles à combustible
- Modélisation thermique des petits satellites
- Analyse électro-vibroacoustique d'un transducteur à armature équilibrée
Consultez les proceedings de la Conference COMSOL 2024
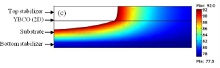
A successful development of an effective quench detection and protection method for a high temperature superconducting (HTS) coil based on a HTS coated conductor tape lays on a thorough understanding of its slowly propagating, three-dimension (3D) quench behavior. Toward this goal, a 3D ... En savoir plus
A contactless electromagnetic principle for the excitation of mechanical vibrations in resonant structures has been investigated. The principle relies on no specific magnetic property of the resonator except electrical conductivity and can be adopted for employing the structures as ... En savoir plus
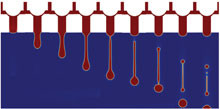
This paper presents a simulation of the operation of a new type of droplet generation probe. This probe, consisting of two concentrically-arranged tubings, is immersed in a beaker of cell medium so that oil is pumped through the outer tubing at a pumping speed less than fluid is drawn ... En savoir plus
Strained wrinkled and flat nanomembranes have different bending properties when they are released from the underlying substrate. This is caused by increased bending rigidity of the wrinkled film in one direction. We provide theoretical and numerical analysis of the directional rolling of ... En savoir plus
The conversion of mechanical energy from environmental vibrations into electrical energy is a key point for powering sensor nodes toward the development of autonomous sensor systems. Piezoelectric energy converters realized in a cantilever configuration are the most studied for this ... En savoir plus
Electromagnetic micro valves are currently developed empirically or the different physics are treated separately. To accelerate the development-process and for a better understanding of the overall system, a multiphysics simulation is built up. This simulation considers the ... En savoir plus
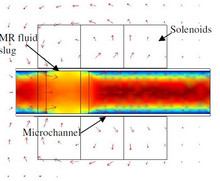
This paper presents the approach taken through the utilization of COMSOL Multiphysics 3.5a, to develop a model that simulates the flow of a magnetorheological (MR) fluid through a micro-channel. The model was developed as an aid in the analysis of a micropump that produces flow by means ... En savoir plus
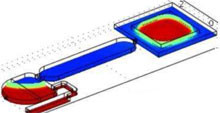
This paper presents an Analog to Digital Microfluidic Converter (ADMC) using passive valves and enabling the conversion of a continuous liquid flow into droplets for Electro-Wetting On Dielectric (EWOD) actuation. Valves calibration, geometry characteristics and losses reduction have ... En savoir plus
A portable device that can identify protein and peptides real time in complex biological systems such as human bodily fluids reliably and accurately is in high demand to properly diagnose and treat medical conditions. Lynntech has developed an innovative Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) based ... En savoir plus
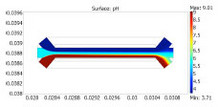
Dielectrophoresis (DEP) is a method for cell manipulation without physical contact in lab-on-chip devices, since it exploits the dielectric properties of cells suspended in a microfluidic sample, under the action of locally generated high-gradient electric fields. The DEP platform that ... En savoir plus